Vehicle telematics insight empowers business owners to improve vehicle management, boost efficiency, track fleets, and prevent downtime. The data is gathered using a telematics device (a black box) and fleet management software to make informed decisions. It enables fleet managers to develop efficient routes and schedule maintenance.
Telematics clubs telecommunications and informatics to benefit the trucking and transportation industry. But to utilize the complete advantage of a vehicle fleet, it is essential to know about telematic systems, their working, and their benefits. Read further to know more.
What is Telematics?
Just like smartphones, what if there are intelligent vehicles? Imagine a smart system installed in your car that can report almost everything from tire pressure, fuel usage and cornering to service warnings and driver alerts. The data will help companies save maintenance costs, improve fuel efficiency, and train drivers about fleet safety.
That is what telematics does. Telematics is a modern system that combines telecommunications and informatics to record data remotely over long distances.
Vehicle telematics employs technology such as GPS sensors and onboard diagnostic codes to acquire fleet data, driver behavior, engine diagnostics, location and activity.
Furthermore, it includes other components that make tracking information easier. These include:
- Accelerometer
- Engine interface
- SIM Card
- GPS device
- Input and output interface
- Buzzer
- Fleet communication software
Although we know why telematics is used, it is equally essential to understand how it helps companies monitor fleets and drivers. Proceeding further, we will throw light on how the system works.
How does vehicle telematics work?
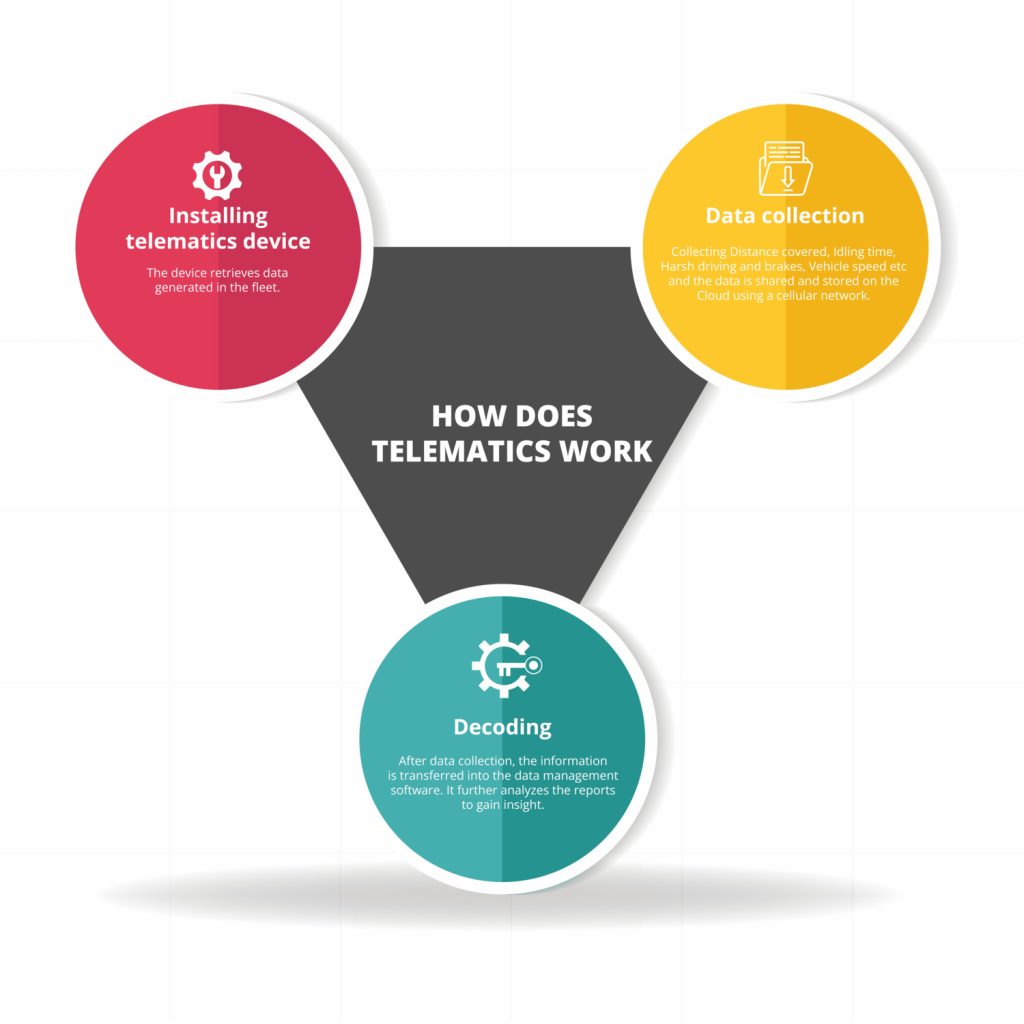
Telematics follows three simple steps:
- Installing the telematics device
- Data collection
- Data deco
1. Installing telematics device
Telematics works through a telematics tracker or device installed in the vehicle. A black box or Onboard Diagnostics Device (OBD) is plugged into the CAN-BUS port in the vehicle. In addition, the system includes a modem and SIM card that allows easy communication using a cellular network to capture important information.
2. Data collection
Once fitted, the device starts retrieving data generated by the vehicle. Everything from GPS, speed, vehicle faults, engine, distance, and other vital information is collected and stored in the cloud.
This data includes:
- Distance covered
- Idling time
- Harsh driving and brakes
- Use of seat belt
- Vehicle position
- Vehicle speed
- Faults, fuel consumption
- Battery usage
- Engine data and more.
3. Decoding
After data collection, the information is transferred into the data management software app. It further analyzes the reports to gain insight into whether a vehicle is due for maintenance, the number of tickets, and drivers who require training.
Car telematics systems employ machine learning and data analytics to extract better value out of connected vehicle data. For instance, the data helps compare performance, better road conditions for commute and structure better routes.
In short, the information generated through the telematics system using a cellular network is stored in cloud servers. Then, it is transferred to data management software for companies to view different parameters.
How is a Telematics Device Installed in an OBD?
Installing an automotive telematics device is not rocket science. It involves plugging the system into your vehicle’s Onboard Diagnostic Port (OBD-II) below the steering wheel. Soon after installation, the device will start recording data about the fleet and driver behavior sharing it via the cellular network.
Apart from OBD-II, a vehicle may also use other telematics systems. Proceed further to learn more about different types of telematics systems.
What are the different types of Vehicle telematics systems?
Technological evolution has enabled telematics to move from closed to open systems. It allows companies to integrate external software, hardware accessories and mobile apps for better operations and efficiency. In addition, it provides integration such as electronic logging (ELDs), remote diagnostics, weather alerts, dash cameras, etc.
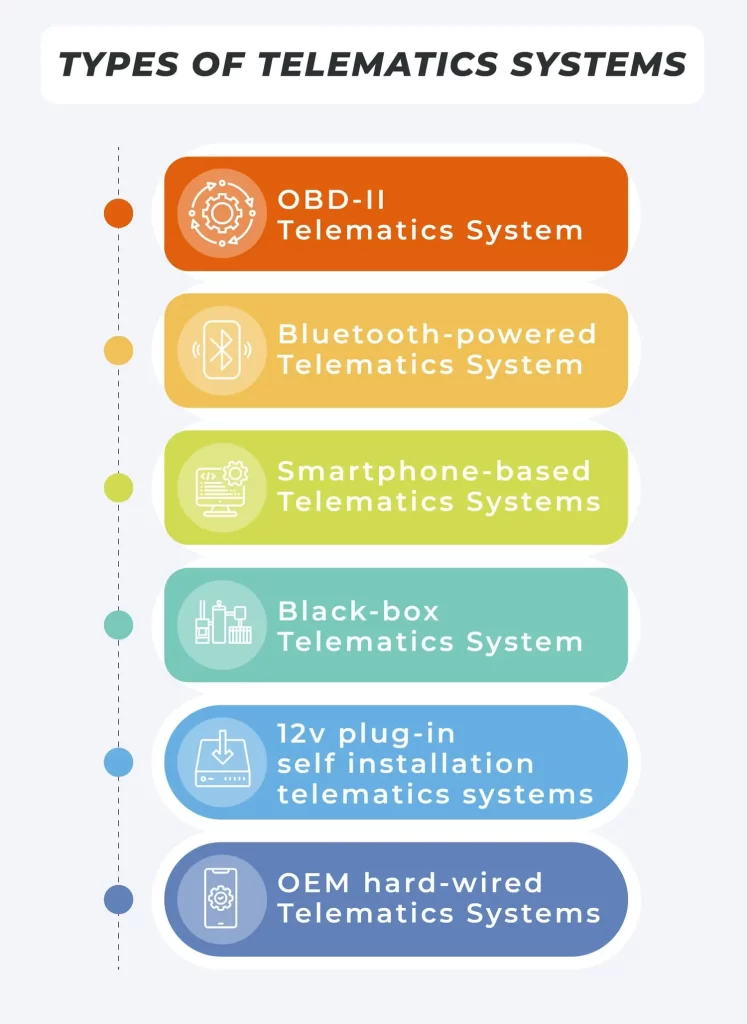
Open-source telematics systems are broadly divided into six types.
These include:
- OBD-II Telematics Systems: Plugged into the vehicle’s onboard diagnostic port
- Bluetooth-powered Telematics Systems: A self-powered data transmission system attached to the vehicle’s center console
- Smartphone-based Telematics Systems: It does not require any setup. It uses a smartphone to collect and transfer data.
- Black Box Telematics Systems: An electrical gadget installed inside the car to collect and transmit data using cell phone connectivity.
- OEM Hard-Wired Telematics Systems: Additional telematics system used to improve functionality and reduce collision severity and frequency.
- 12v Plug-in Self-Installation Telematics System: Plugged into the car’s 12v socket and may require technician assistance.
How Does Telematics Data Work?
Telematics data gathered from the device is shared on a central system and allows companies to use the information for making informed decisions. It helps analyze risks, improvement areas, driver behavior, and road conditions to implement efficient services.
Which Sectors and Businesses Can Use Telematics?
Telematics can be applied to a wide range of industries. It is commonly applied in the logistics and transportation industry, agriculture, insurance, healthcare, energy, retail, and more.
Advantages of Using Telematics in Fleet Management
Vehicle telematics encompasses six core areas of fleet management. A brief insight of each includes:
-
Fleet Optimization
Enables optimization fleet maintenance. It tracks idling, and fuel consumption, and streamlines predictive maintenance abilities, fuel management, and remote diagnostics.
-
Safety
Works towards increasing safety by enabling driver coaching, reporting driver behavior, sharing collision notifications, reconstruction and locating stolen vehicles.
-
Productivity
Improvised customer service using real-time data through GPS tracker, dispatching, trip reporting and routing tools.
-
Expandability
Allows integrating other software systems using cellular networks to gain insight into wide information.
-
Compliance
Enables electronic logging, tracking hours of service, scheduling vehicle inspections and IFTA reporting.
-
Sustainability
Helps manage electric vehicles, reducing environmental impact and carbon emissions, and helps to develop and maintain sustainable smart cities.
How to choose a vehicle telematics solution for industrial fleet management?
Selecting an appropriate telematics solution is essential to streamline businesses. Factors to consider when choosing a fleet telematics system:
The telematics system you choose must be reliable and flexible in ensuring smooth data delivery. A good telematics solution must
- Provide good visibility
- Gather real-time vehicle data
- Simplify workflow and track vehicle performance
- Increase vehicle safety by reporting risk and analyzing incidents
- Provide options for vehicles, managers and drivers to optimize the functionality
- Seamless integration of the system with vehicles
A good telematics solution provider will provide constant assistance. The system will help automate processes, track metrics and improve the overall efficiency to tackle fleet management challenges.
What are the benefits of telematics in the Insurance industry?
Telematics allows auto insurers to gain insight into driver behavior. It helps insurance companies track, store and transfer driving-related data and customizes vehicle insurance rates accordingly. For example, usage-based data or UBI telematics allow the insurance industry to know about the distance covered, speed, how frequently the vehicle is used, rash driving, harsh brakes and much more to understand overall driver behavior.
Based on the data gathered, a safe driver is charged low premium charges and personalizes premiums after analyzing data and reports.
What are the challenges of Vehicle Telematics?
Major challenges of vehicle telematics include:
- Increasing software costs
- Data integration and data sharing
- Meeting customer requirements
Conclusion
Telematics is becoming an essential aspect of the automobile, insurance, and fleet industries. It helps save costs that outweigh the cost of installation, maintenance, and management of technology. In addition, more companies are recognizing the need for monitoring fleet activities, improving accountability, and maintaining compliance with government regulations.
Further, mobile telematics can help reduce costs, improve efficiency, and gain more valuable insight, as compared to traditional devices.
Are you ready to transform your business using telematics data? CerebrumX provides a platform for companies to use Usage Based Insurance programs to improve fleet efficiency and provide personalized services.